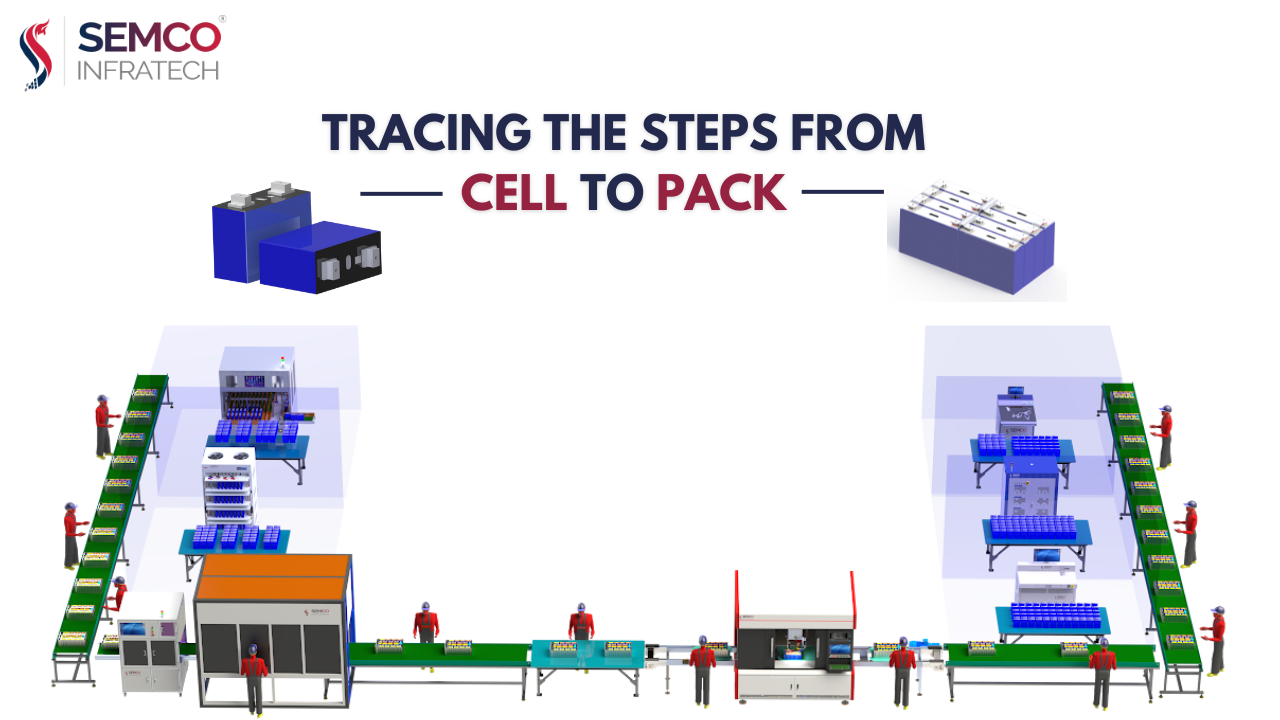
The production of lithium battery modules, also known as Battery Packs, involves a meticulous and multi-step manufacturing process. This article outlines the key points of the lithium battery module PACK manufacturing process, emphasizing the critical stages contributing to the final product’s efficiency, consistency, and safety.
Selection and Matching Group
One of the initial steps in lithium battery module manufacturing is the selection and matching of battery cells. This involves sorting batteries based on various parameters such as internal resistance, open-circuit voltage, rated capacity, and charge/discharge efficiency. The goal is to achieve a high level of consistency in the internal characteristics of the batteries, improving module efficiency and extending its service life.
Lithium Battery Cell Assembly Fixture:
The assembly of lithium battery cells requires precision and careful handling. An automatic spot-welding machine is employed to assemble cells in the correct order, avoiding short circuits. After welding, the battery pack undergoes quality checks to identify and rectify any welding defects.
An automatic spot-welding machine, employed with the assistance of automation and robotics, assembles cells in the correct order, minimizing human error and streamlining the process. After welding, the battery pack undergoes rigorous quality checks, including visual inspections and electrical testing, to identify and rectify any defects before proceeding.
Lithium Battery Pack Welding PCM/BMS:
The Protective Circuit Module (PCM) or Battery Management System (BMS) is a crucial component in ensuring the safety of lithium battery packs. PCM with a balance function is selected for low-voltage packs, while high-voltage packs may require advanced BMS. Proper soldering and inspection of connection points are vital to guarantee the quality and safety of the battery pack.
Semi-finished Insulation:
This stage involves the fixation and insulation of voltage acquisition wires, ensuring the safety and integrity of the battery pack. Various materials, including high-temperature adhesive tape and epoxy board, are used to prevent extrusion damage and short circuits.
Semi-finished Product Testing:
After adding the BMS, the semi-finished battery pack undergoes comprehensive testing, including charge and discharge tests, internal resistance tests, overcharge tests, and more. Specialized tests, such as high and low-temperature tests and drop tests, are recommended for random inspection to ensure the durability of the lithium battery pack.
Following the BMS installation, the semi-finished battery pack undergoes comprehensive testing, encompassing charge and discharge cycles, internal resistance checks, overcharge tests, and more. Robust quality control measures, implemented throughout the process, utilize visual inspections, electrical testing, and thermal imaging to ensure the safety and reliability of the final product.
PACK Packaging:
Depending on the design, this step involves careful packaging of the battery pack to prevent collision or extrusion. Insulation of positive and negative electrodes is essential, and various packaging methods such as PVC wrapping or ultrasonic sealing are employed.
The Whole Set of Tests:
Parameters are set, and the whole set of testers is employed to assess critical aspects such as shipment voltage, internal resistance, and charging/discharging capabilities. Alternative tests for overcurrent and short circuits ensure the battery pack’s overall performance.
Packing and Shipping:
Proper packing is crucial to avoid transportation damage. Foam cushioning, especially for large battery packs, is essential. Wooden racks may be used for additional safety during transportation.
Conclusion
Tracking and controlling each stage of the lithium battery module PACK manufacturing process is essential for ensuring quality and safety. Skilled employees, strict procedures, automation, and robotics enhance efficiency and reliability. Sustainable practices like recyclable materials and energy-efficient equipment are becoming more important. Future advancements include chemistries, solid-state batteries, and the integration of artificial intelligence for process optimization.