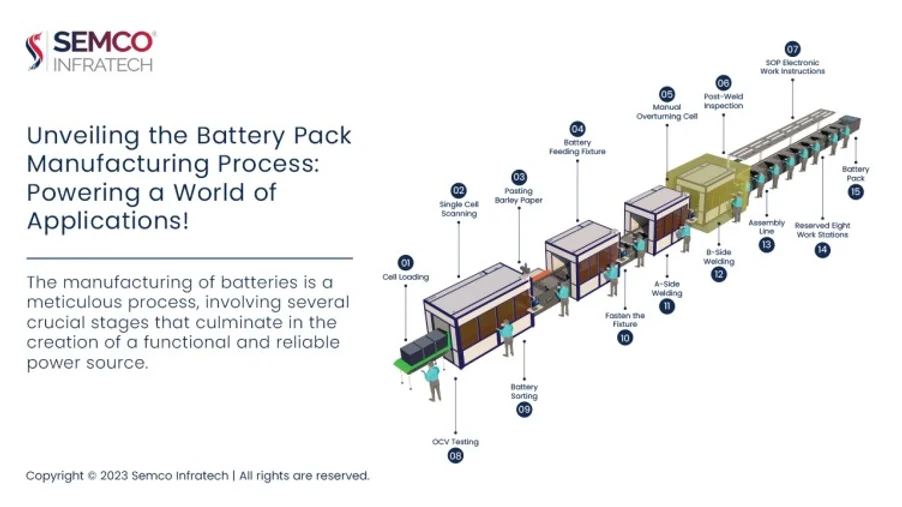
In the relentless pursuit of advancing battery technology, the shape and structure of lithium-ion batteries play a pivotal role. These batteries come in three primary forms, each with unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Here we will discuss Lithium-ion Batteries: Cylindrical, Prismatic, or Pouch. Notably, in recent years, the market has witnessed a significant surge in the popularity of pouch batteries, hinting at a potential market takeover, with experts predicting that the market share of pouch batteries will soon surpass 50%.
The Triad of Lithium-ion Batteries

Cylindrical Batteries: Proven and Prolific
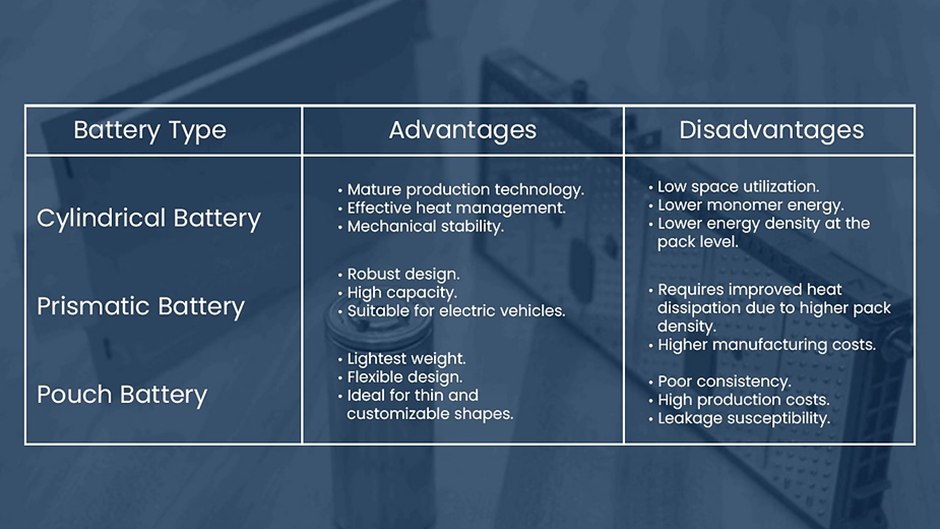
Cylindrical lithium-ion batteries come in various models, such as 14650, 17490, 18650, 2170, and 26500. These batteries have a well-established production process, offering low PACK costs and high yield, ensuring consistency across battery packs.
With its ample heat dissipation area, the cylindrical form outperforms prismatic and pouch batteries in terms of thermal management. The mature production of these batteries is seen in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and the United States.
While cylindrical batteries have gained acclaim for their reliability, they tend to be heavier, less space-efficient and offer relatively low energy density at the pack level.
With the growing demands of the electric vehicle market, there’s a push to increase the size of cylindrical batteries, aiming to extract more battery capacity.
Prismatic Batteries: Bigger and Bolder
Prismatic batteries are encased in materials like aluminum alloy, and stainless steel, and are assembled through winding or lamination.
They excel in safety and flexibility, and their design allows for easy assembly of high-capacity batteries.

Prismatic batteries boast higher pack density but require improved heat dissipation due to the smaller gap between cells.
The transition from steel shells to aluminum shells has gained momentum, given their lightweight, safety, and performance advantages. These batteries find extensive application in electric vehicles and are renowned for their robustness.
Pouch Batteries: Market Dominance on the Rise
Pouch batteries maintain traditional cathode and anode materials but differ in their flexible packaging material, typically an aluminium-plastic composite film.
This unique packaging material accounts for their lighter weight, making them 40% lighter than steel-shell batteries and 20% lighter than aluminium-shell batteries of the same capacity.
The flexible design of pouch batteries allows for variable shapes and thinness, facilitating the development of new battery models tailored to customer needs.
However, pouch batteries grapple with issues of poor consistency, higher production costs, and susceptibility to leakage, challenges that can be mitigated through scale and quality improvement.
Pouch batteries find extensive use in consumer electronics like smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
Comparing the Three Batteries
Conclusion
Each of these battery types serves as a pioneer in its respective field, driving fierce competition in the battery market. Cylindrical batteries have found their niche in power tools, toys, lamps, automobiles, electric bicycles, and portable mobile energy systems. Pouch batteries are well-suited for smartphones, drones, laptops, and wearable devices due to their lightness and customizable shape. Prismatic batteries stand tall in the realm of electric vehicles, including industrial trucks, forklifts, power grid energy storage, and medical equipment.
With a multitude of shapes and sizes, the future of lithium-ion batteries is as diverse as the technology they power. Each variant brings its strengths and innovations to the table, ensuring that the world of battery technology continues to evolve and adapt to our ever-changing needs.